By Collins Odhiambo Owino
Author | DatalytIQs Academy
Data Source: Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) – Kenya Data Portal
Overview
Kenya’s external trade data paints a fascinating picture of an economy deeply integrated with global markets. From industrial imports to tea and coffee exports, the balance of trade reveals both opportunities and vulnerabilities in the country’s economic structure.
The Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) dataset (December 2024 – September 2025) highlights three key trends:
-
Export performance (domestic and re-exports)
-
Import composition by category
-
Import sources by continent
1. Export Trends: Modest Growth, Limited Diversification
Kenya’s exports averaged around KSh 100 billion per month during the first three quarters of 2025.
-
Domestic Exports: Continue to dominate, led by tea, coffee, horticulture, and apparel.
-
Re-exports: A steady but smaller share, showing Kenya’s emerging role as a trade hub.
-
Overall Growth: Exports grew slightly from December 2024 to April 2025, before flattening due to subdued global demand.
Insight: Kenya remains heavily reliant on agricultural exports, leaving the economy exposed to global commodity price shocks.
2. Import Patterns: Industrial and Energy Dependence
Monthly imports exceeded KSh 220 billion, with several key categories dominating:
-
Industrial Supplies (Non-Food): The largest share, indicating reliance on foreign raw materials.
-
Fuel and Lubricants: Second-largest component, reflecting energy import dependence.
-
Machinery & Transport Equipment: High due to ongoing infrastructure and manufacturing projects.
-
Consumer Goods: Reflecting growing domestic demand and limited local substitution.
Result: The average trade deficit stood near KSh 120 billion per month — a structural challenge that affects the exchange rate and foreign reserves.
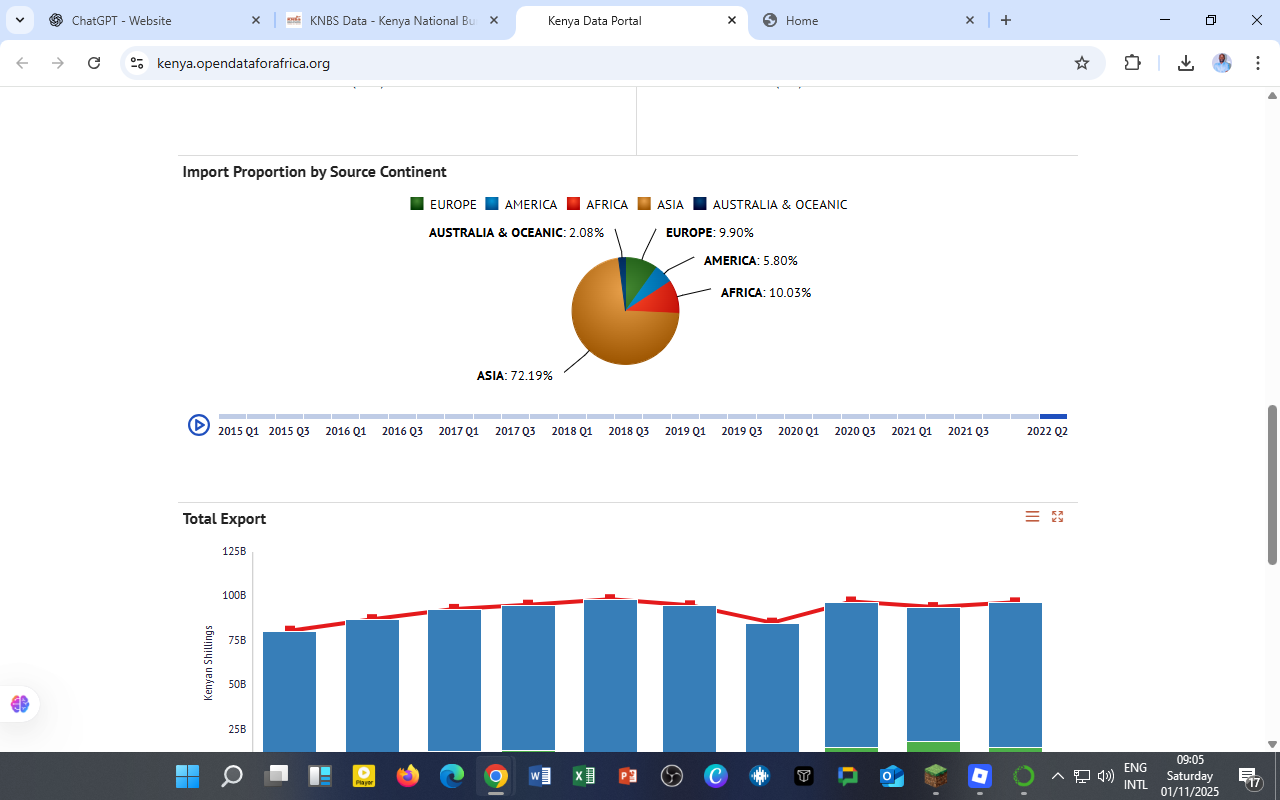
3. Import Proportion by Source Continent
The geographic breakdown of Kenya’s imports highlights a striking dependence on Asia, which supplies 72.19% of total imports.
| Continent | Share of Imports (%) | Major Source Countries |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | 72.19 | China, India, Japan, UAE |
| Africa | 10.03 | South Africa, Egypt, Tanzania |
| Europe | 9.90 | Germany, UK, Netherlands |
| America | 5.80 | USA, Brazil |
| Australia & Oceania | 2.08 | Australia, New Zealand |
Observation:
Asia’s dominance reflects Kenya’s strong import ties with China and India, particularly in machinery, electronics, textiles, and fuel products.
4. Trade Balance and Economic Outlook
| Indicator | Average (KSh Billion) | Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Total Exports | 100 | Slight increase Q1–Q2 |
| Total Imports | 220 | Stable, slight rise Q3 |
| Trade Deficit | 120 | Persistent imbalance |
Economic implications:
-
The wide trade gap puts pressure on Kenya’s foreign exchange reserves and shilling value.
-
Overreliance on Asia limits supply chain diversification.
-
Export stagnation calls for value addition and regional market expansion.
5. Policy Recommendations
To build a sustainable trade structure, Kenya should:
✅ Incentivize local manufacturing of industrial inputs.
✅ Promote renewable energy projects to reduce fuel imports.
✅ Develop export value chains in agriculture and technology.
✅ Strengthen intra-African trade through AfCFTA frameworks.
For DatalytIQs Academy Learners
This dataset offers hands-on analytical learning opportunities:
-
Compute import–export ratios and visualize the trade deficit trend.
-
Analyze continent-wise trade dependence using pie charts and bar plots.
-
Forecast trade performance using ARIMA or Prophet models in Python.
-
Correlate trade data with GDP, inflation, or currency trends for deeper insights.
Data Source and Acknowledgment
Dataset: External Trade (Exports, Imports, and Import Sources, 2024–2025)
Source: Kenya Data Portal – KNBS External Trade
Acknowledgment: Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) and the African Development Bank for promoting open data and transparency in African economies.
Author: Collins Odhiambo Owino, DatalytIQs Academy.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.