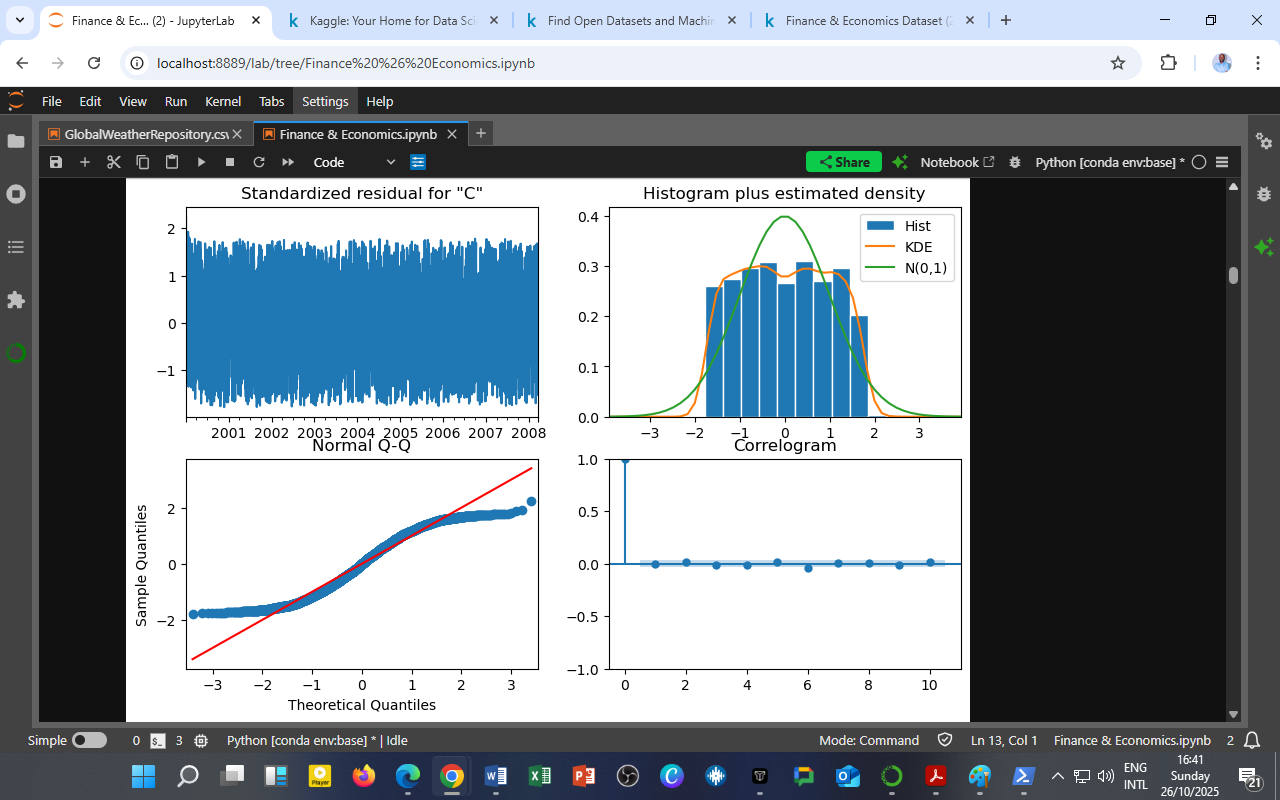
 To evaluate the robustness of the ARIMA(2,1,2) model, a residual diagnostics test was performed. The four-panel output above provides an in-depth look at the model’s error behavior, ensuring that it meets the classical assumptions of time-series modeling — normality, independence, and homoscedasticity.
To evaluate the robustness of the ARIMA(2,1,2) model, a residual diagnostics test was performed. The four-panel output above provides an in-depth look at the model’s error behavior, ensuring that it meets the classical assumptions of time-series modeling — normality, independence, and homoscedasticity.
Diagnostic Components Explained
-
Standardized Residuals (Top Left)
The residuals fluctuate randomly around zero without any visible pattern.
This indicates that the model has captured the underlying structure of the data, leaving only white noise (random error). -
Histogram plus Estimated Density (Top Right)
The histogram of residuals (blue) closely follows the overlaid normal distribution (green curve).
The residuals are approximately normally distributed, suggesting that the ARIMA model’s error term behaves as expected under Gaussian assumptions. -
Normal Q–Q Plot (Bottom Left)
The plotted residual quantiles align closely with the theoretical normal line (red).
Confirms that deviations from normality are minimal, and the residuals follow a nearly normal distribution across quantiles. -
Correlogram (ACF Plot, Bottom Right)
The autocorrelation function (ACF) shows no significant spikes beyond the 95% confidence bounds.
The residuals are serially uncorrelated, meaning that the model successfully removed temporal dependencies in the time series.
Analytical Insight
The diagnostic tests collectively validate that the ARIMA(2,1,2) model is statistically sound:
-
Errors are random and independent (no leftover autocorrelation).
-
The residual variance is constant over time.
-
Residuals follow a normal distribution, satisfying assumptions for forecasting accuracy.
This means the model is suitable for generating short-term stock price forecasts, volatility projections, and risk simulations with confidence intervals grounded in proper statistical behavior.
Practical Application
Residual diagnostics such as these are essential in professional econometrics, especially before deploying predictive models in:
-
Algorithmic trading,
-
Economic forecasting, or
-
Financial risk management.
At DatalytIQs Academy, this step is emphasized as a crucial stage in ensuring analytical integrity — turning models into trustworthy decision-support tools.
Source & Acknowledgment
Author: Collins Odhiambo Owino
Institution: DatalytIQs Academy
Dataset: Finance & Economics Dataset (2000–2025), Kaggle.
Source: DatalytIQs Academy Research Repository — compiled from international financial and economic databases (2025).
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.