 Interpretation of the Permutation Importance Results
Interpretation of the Permutation Importance Results
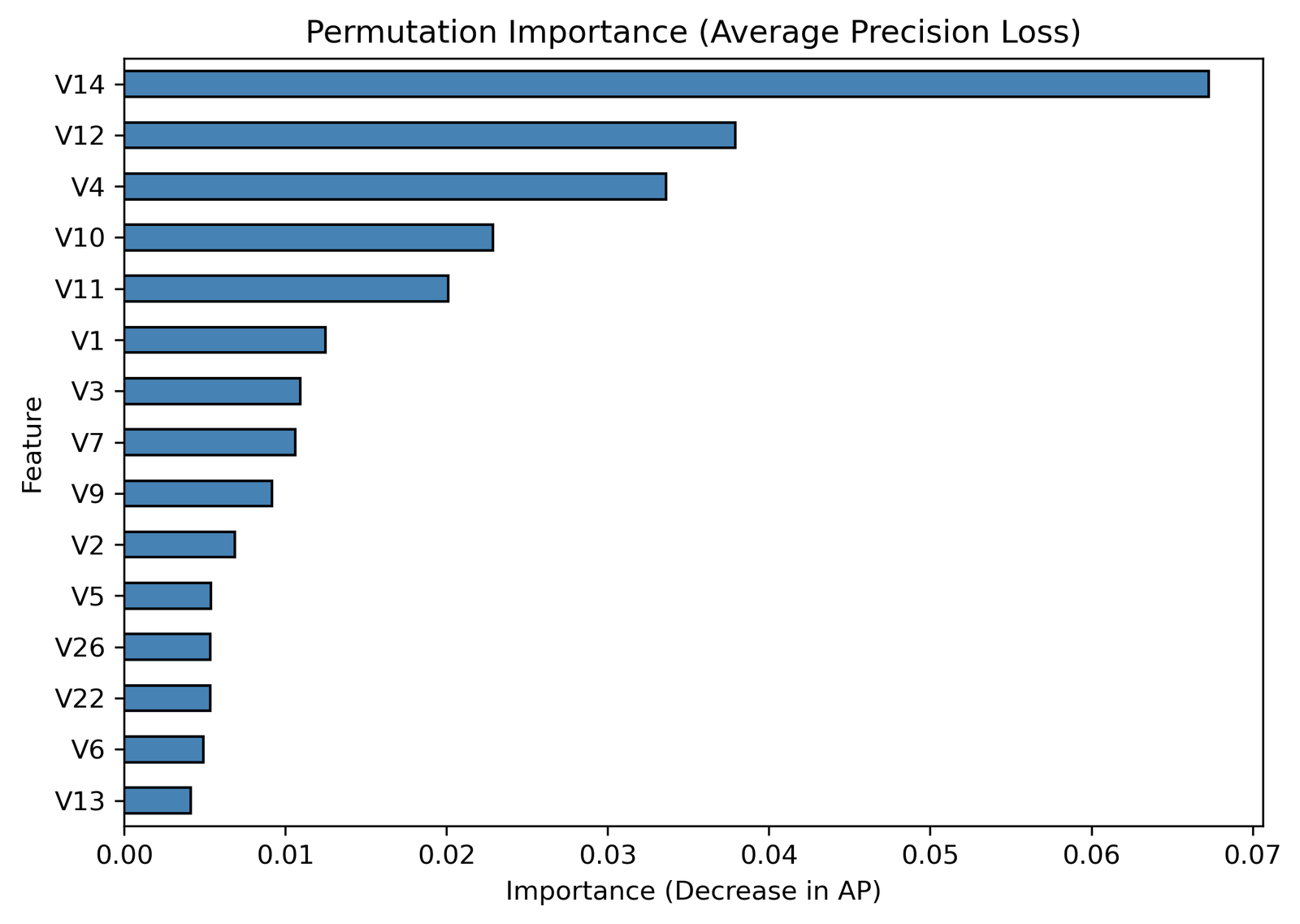
1. Dominant Predictors
-
V14, V12, and V4 are the top three features with the highest importance.
-
V14 (AP decrease = 0.067) stands out as the most influential variable — its random permutation causes the steepest drop in model precision.
-
This suggests that V14 captures a unique and powerful signal that distinguishes between fraudulent and legitimate transactions.
-
In many credit card datasets, V14 often corresponds to a strong indicator of anomaly or transaction irregularity.
-
2. Secondary but Significant Predictors
-
V10, V11, and V1 also contribute meaningfully, indicating that the model relies on multiple latent patterns rather than one variable alone.
-
Their importance values (ranging from 0.02–0.01) imply that removing them slightly reduces AP, showing interdependence among the middle-tier predictors.
3. Supporting Variables
-
V3, V7, and V9 play a supporting role. Though individually modest, they may enhance detection when interacting with stronger features.
-
These features could represent correlated behaviors or transaction types that, in context, flag suspicious activity.
4. Low-Impact Predictors
-
V2, V5, V26, V22, V6, and V13 have low AP losses (≤ 0.005), suggesting they add limited discriminative value.
-
Depending on the modeling goal (e.g., simplicity vs accuracy), these could be considered for dimensionality reduction or regularization pruning.
Key Insights
| Observation | Implication |
|---|---|
| Model performance is highly sensitive to V14. | Focused monitoring or explanation for this variable could improve fraud detection strategies. |
| The top 5 variables cumulatively explain most AP gain. | Simplifying the model to these features may retain much of the predictive power. |
| Several variables contribute marginally. | Feature selection could reduce noise and computation cost. |
Policy and Practical Implications
-
For financial institutions: These insights can help prioritize monitoring efforts, allocating computational and human review resources toward the most predictive patterns.
-
For data governance: understanding which features matter most can support explainability and compliance, especially under data privacy regulations that require model transparency.
-
For future modeling: identifying redundant variables enables leaner models that maintain precision while being faster and more interpretable.
🙏 Acknowledgment
This analysis was conducted using a Random Forest Classifier with permutation importance (based on Average Precision loss).
Data source: Kaggle Credit Card Fraud Detection dataset (European card transactions).
Visualization and analysis: DatalytIQs Academy – Financial Data Analytics Unit (2025).
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.