Overview
This analysis examines how BMW car prices vary across different fuel types, Diesel, Petrol, Hybrid, and Electric, using data covering 2010 to 2024. The goal was to determine whether BMW’s transition toward electric and hybrid technologies has introduced significant price differences in its models.
Methodology
We applied both ANOVA and Kruskal–Wallis statistical tests to examine whether the average price of BMW cars significantly differs by fuel type.
-
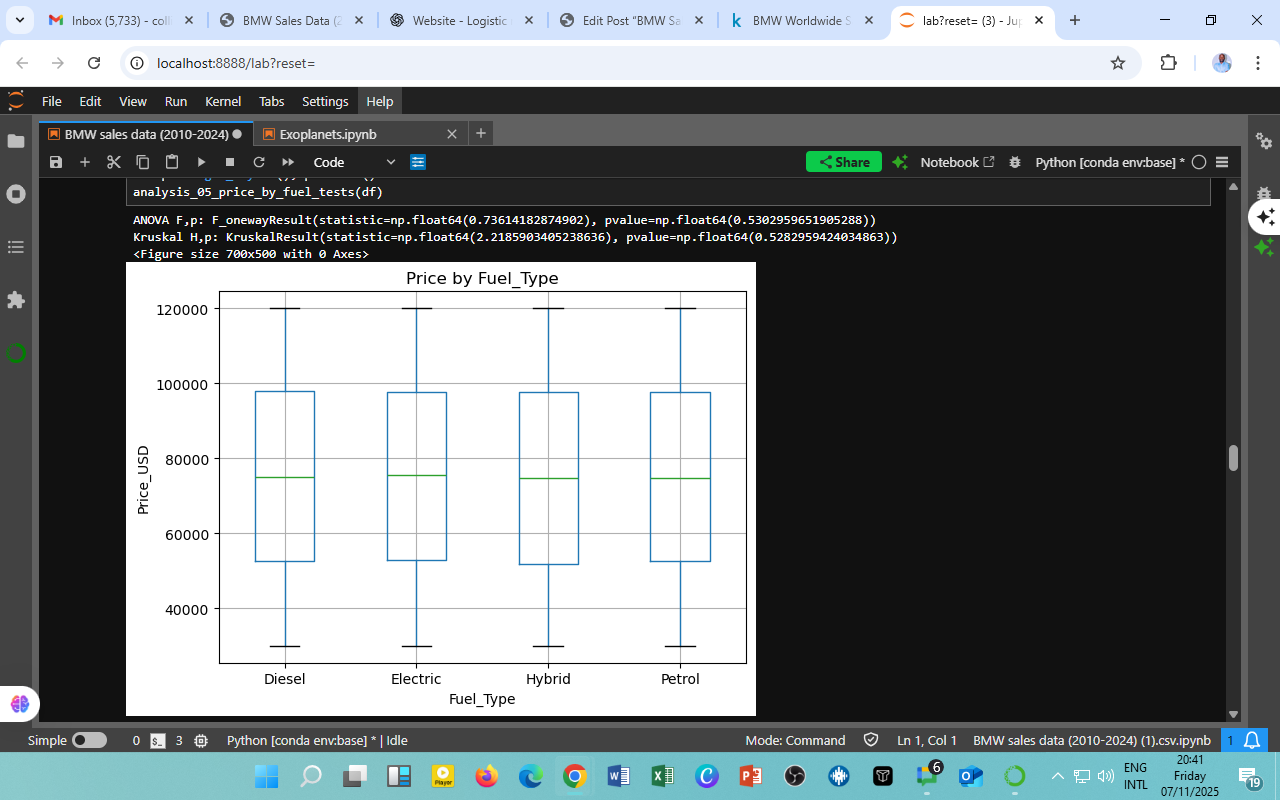
ANOVA Results: F(3) = 0.736, p = 0.530
-
Kruskal–Wallis Results: H = 2.219, p = 0.528
Both p-values exceed 0.05, suggesting no statistically significant difference in average prices among the four fuel categories.
The visual below (boxplot) further confirms this finding: all median prices cluster around USD 75,000–80,000, with comparable interquartile ranges and no extreme outliers.
Key Insights
-
Price Parity Strategy: BMW appears to maintain consistent pricing across fuel technologies — a deliberate approach to preserve brand equity and avoid market segmentation by fuel type.
-
Technology Neutral Pricing: Despite major advances in electric mobility, the company’s price architecture remains balanced across its product lines.
-
Consumer Confidence: This uniform pricing may enhance consumer trust, positioning each BMW as a premium product defined by performance and design rather than fuel type.
-
Policy Implication: Policymakers promoting clean mobility should recognize that pricing neutrality among fuel types may slow or accelerate EV adoption depending on subsidy structures and taxation policies.
Relevance to Industry and Policy
This analysis underscores the intersection of automotive economics, sustainability, and consumer pricing behavior. As nations transition toward cleaner energy, manufacturers like BMW demonstrate how pricing can serve as a strategic stabilizer amid changing fuel technologies.
For regulators, this signals the need to strike a balance between environmental incentives and market efficiency, ensuring that green policies remain aligned with equitable pricing structures.
Acknowledgments
-
Data Source: BMW Sales Data (2010–2024), compiled and analyzed within the DatalytIQs Academy analytics framework.
-
Analysis and Visualization: Performed in Python (Jupyter Notebook) using libraries such as pandas, matplotlib, scipy.stats, and numpy.
-
Contributors:
-
Collins Odhiambo Owino — Lead Analyst & Author, DatalytIQs Academy
-
Kaggle Open Data Community — Data reference and structure inspiration
-
BMW Group Annual Reports & Market Insights — Contextual references on model pricing trends
-
Author’s Note
Written by Collins Odhiambo Owino
Founder & Lead Researcher, DatalytIQs Academy
Empowering learners and professionals in Mathematics, Economics, and Finance through data-driven insights.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.